Main Organs Involved in COVID-19
Olive Martin
DOI10.36648/2576-3903.5.3.10
Olive Martin*
Insight Medical Publishing, 483, Green Lanes, London, N13 4BS, UK
- *Corresponding Author:
- Olive Martin
Insight Medical Publishing, 483
Green Lanes, London, N13 4BS, UK
Tel: +1-702-508-2676
E-mail: contact@imedpub.com
Received date: August 03,, 2020; Accepted date: August 10, 2020; Published date: September 10, 2020
Citation: Martin O (2020) Main Organs Involved in COVID-19. J Neoplasm Vol.5 No.3:10.
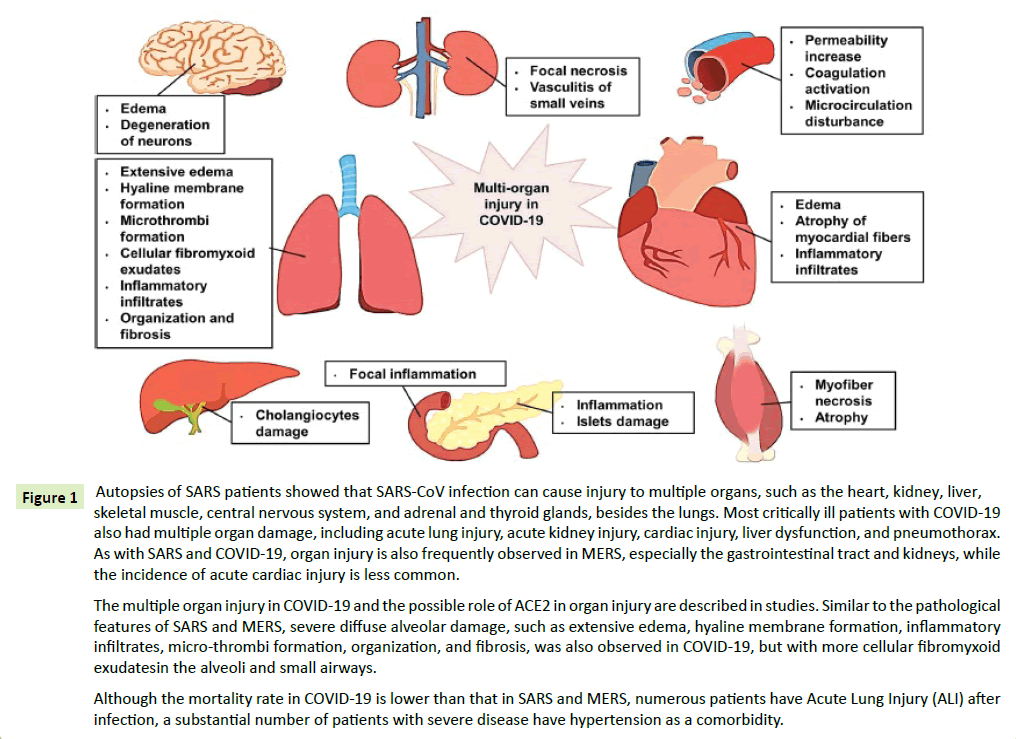
Figure 1: Autopsies of SARS patients showed that SARS-CoV infection can cause injury to multiple organs, such as the heart, kidney, liver, skeletal muscle, central nervous system, and adrenal and thyroid glands, besides the lungs. Most critically ill patients with COVID-19 also had multiple organ damage, including acute lung injury, acute kidney injury, cardiac injury, liver dysfunction, and pneumothorax. As with SARS and COVID-19, organ injury is also frequently observed in MERS, especially the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys, while the incidence of acute cardiac injury is less common.
The multiple organ injury in COVID-19 and the possible role of ACE2 in organ injury are described in studies. Similar to the pathological features of SARS and MERS, severe diffuse alveolar damage, such as extensive edema, hyaline membrane formation, inflammatory infiltrates, micro-thrombi formation, organization, and fibrosis, was also observed in COVID-19, but with more cellular fibromyxoid exudatesin the alveoli and small airways.
Although the mortality rate in COVID-19 is lower than that in SARS and MERS, numerous patients have Acute Lung Injury (ALI) after infection, a substantial number of patients with severe disease have hypertension as a comorbidity.

Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences